Ultimate Guide to Google Display Network in 2022



Ready to unlock new revenue heights with pay per click advertising? Want to elevate your online ads and reach new audiences?
There is one incredible side to Google Ads, formerly known as Google Adwords, that can deliver incredible results:
Display advertising on the Google Display Network (GDN).
When it comes to Google Ads, marketers often focus their energy entirely on the Search Network. And for good reason – Google’s search ads can deliver an incredible, rapid return on investment.
But waiting for customers to actively search for what you offer is simply one piece of the puzzle. That’s why the GDN can be a great addition to your digital advertising strategy.
GDN provides incredible conversions and brand awareness – if you know how to use it properly.
The good news is, getting success with display advertising isn’t as complicated as many marketers think. You simply need to know how to approach it and use proven tips for display ads. That’s why we’ve created this article to answer all your GDN questions.
Ready to get results from display advertising? This Google Display Network Guide is for you.
What is Google Display Advertising?
Display ads are image-based and target those interested in your items but aren’t actively searching for them. In contrast, search advertisements are text-based and allow you to target specific keywords.
When browsing your mobile app or favorite websites, you’re likely to come across display campaigns.
They may, however, display in your Gmail account, applications, or videos.
Best used for: Reaching out to potential customers early in the purchase cycle, raising brand recognition and website traffic.
Display advertising can help you present your company to specific target groups that are likely to be interested in what you have to offer.
In this manner, you may reach a more significant number of individuals than if you solely used search advertisements.
You may show your advertisements on the Google Display Network, a compilation of over 2 million sites that reach over 90% of internet users worldwide, using Google Ads.
Nonetheless, you expose your company to a specific target group that is likely interested in your products or services. This may enable you to reach a more significant or whole new audience than would otherwise be possible through search.
Standard display ads are an excellent option for individuals looking to expand their company and reach a larger audience.
Using Google Display Advertising, you can target audiences and filter them based on their interests and demographics, ensuring that your advertisements are served to people who are likely to convert.
What is the Google Display Network?
The Google Display Network is a network of millions of sites where advertisers can show their display ads.
Whether you’re just browsing the internet, checking your Gmail, or watching your favorite videos, the Google Display Network will present display ads it deems relevant to you while you do almost anything online.
The Display Network allows visual and rich media ads instead of just plain text ones. Considering that the human brain processes images 60,000 times faster than text, that alone can be a pretty big game-changer.
Where do Google Display Ads appear?
When you use Google ads to promote, your ads display in various locations throughout the web based on how you target your display network campaign, who you choose to show them to, and the sorts of display ads you generate. You can also perform conversion tracking in your google ads account.
This page explains where your advertising may appear and who may view them:
On Google and other search engines
When customers search for the product or service you provide, your ad may display on Google. When creating your ad, you’ll select a list of keywords—the words or phrases that will cause your ad to appear. When visitors search for the terms or phrases you chose, your text advertising may show alongside or above the search results.
Google search sites: Ads on Google Search can show above or below search results. Display ads may appear beside, above, or even below results pages on Google Play, in the Shopping tab, and on Google Maps, including the Maps app.
Google search partners: Ads may display alongside search results on Google search partners’ websites. Search partners for text advertising include hundreds of non-Google websites, Google Video, and other Google sites.
On websites where your consumers browse
You may also opt to display ads to individuals as they explore the web. Your text, picture, and video advertisements may be displayed on the Google Display Network.
The Display Network is a network of websites that display advertisements, including Google services such as Google Finance, Gmail, Blogger, and YouTube. Mobile sites and applications are also part of this network.
If you’ve ever wondered how an ad on your favorite news site or in your Gmail account got there, now you know: these sites are members of the Google Display Network.
Depending on the targeting options you select, your adverts may display on websites. There are numerous ways to target your adverts on the Display Network:
- Choose keywords and subjects that are relevant to what you have to offer.
- Select one or more websites or pages.
- Choose in market audiences based on their interests, demographics, or previous visits to your website. Find out where your advertising could show on the Display Network.
On various devices
Display ads can also be shown to individuals when they are searching for or visiting websites on the go:
When users use their mobile devices or tablets to search on Google, your text advertising may display.
When users visit Google Display Network websites using high-end mobile devices like iPhones, Android smartphones, or tablets, your text, picture, and video ad may show.
Your advertising may also display in mobile applications that are part of the Display Network.
In certain regions or languages
You may opt to show text advertising to consumers in an entire nation, a specified geographic region, or even customers who use place names in their searches if you have them.
You may also tailor your display campaigns to your potential clients’ languages to reach them more effectively. Suppose your clients speak more than one language. In that case, you may set up different campaigns to handle advertising and keywords in each of those languages.
What is a display ad?
A display ad is carefully integrated into chosen websites, where it can reach users while they shop, browse or read.

What is an example of a display ad?
While there are many different ad formats and types of display ads, the one most people would recognize first would be a banner ad:


Banner ads are typically either static images, animated images such as GIFs, or videos. You can usually find a banner ad placed at the top or bottom of a web page, for example:
But you can also see a banner ad interspersed within the content itself such as this:
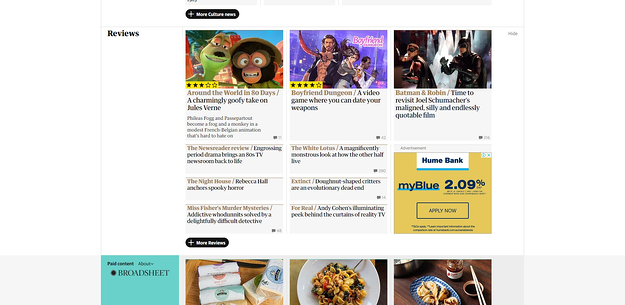
What are the types of Google Display Ads?
The following are some of the ad kinds available on the Google Display Network:
Uploaded Display Ads
Ads that are uploaded are generated outside of Google display Ads using a program such as Google Web Designer. They may be posted to Google Ads as a.zip file, GIF, JPG, or PNG.
You have total creative control over your Display Network campaigns when creating and submitting your own picture advertising.
Google Ads accepts the following ad types for upload: image (e.g., GIF, JPG, PNG), AMP HTML, and HTML5.
Note: If you need to change an existing HTML5 ad, you must re-upload it as a new ad with its own set of reports.
Advantages of Uploaded Ads
You have total control over how your advertisements appear when you develop your own advertising in Google Web Designer. You may create these ads yourself by using templates and deciding how to best mix your various photos, text, and logos. These adverts can be linked to a feed for dynamic remarketing.
HTML5 advertisements that have been uploaded may also be made responsive by defining how your advertising should be scaled throughout the Google Display Network.
Because uploaded advertising is developed outside of Google Ads, it will not appear in all areas of the Display inventory, unlike responsive display ads.
Making Use of Google Web Designer
Google Web Designer may be used to create rules that will make your uploaded HTML5 advertisements responsive, which means that Google will show your ads in a variety of sizes and aspect ratios (for example, adjusting your ad to appear in landscape or portrait).
Responsive Display ads + Video ads
Responsive ads offer you to upload your assets (images, headlines, logos, videos, and descriptions). Google will develop ad combinations for websites, applications, YouTube, and Gmail automatically. Display campaigns can take advantage of responsive display adverts.
Turn on YouTube captions to view subtitles in your language. At the bottom of the video player, click the “Settings” icon, then choose “Subtitles/CC” and pick your language.
Benefits
Optimise your advertisements: When you upload multiple assets into Google Ads to build a responsive display ad, Google utilises a machine learning model to find the ideal combination of assets for each ad slot based on predictions developed from your performance history.
Use with videos: Include videos in your responsive display advertising to increase your visibility on the Display Network. When Google Ads deems that videos may drive more excellent performance for you, they will be presented instead of photos.
Save time: By using responsive display ads, you may decrease your overhead for maintaining ad portfolios inside ad groups and campaigns, allowing you to devote more effort to performance optimisation.
Use with feeds: Responsive display ads provide tailored material to customers based on a feed that you control and contribute to your campaign. When you include a feed in your campaign, your advertising will appear in dynamic and static versions.
Video Ads
Display Network advertising in video placements can reach millions of prospective buyers. These advertising enable you to broaden your brand’s reach internationally across a wide range of demographics via YouTube and Google’s video publishing partners.
Benefits
Increase brand recognition: Video placements are a fantastic approach to increase brand awareness, especially on highly visible platforms like YouTube and drive more website traffic.
Increase traffic to your website by targeting specific video placements or YouTube with your existing text and picture advertising.
What are the benefits of Google display ads?
The following are the advantages and worth of Google Display Advertising:
Reach a Large Audience
The main advantage of Google Display ads is its ability to reach many people throughout the Google network.
Display advertising provides an obvious advantage for firms looking to boost their visibility and reach more consumers online.
Reduced Cost Per Click
The cost-per-click (CPC) of your ads can make or break your display advertising budget. If the cost per click is high, the entire budget will be depleted with just a few clicks. However, keeping the cost per click low will obtain more valuable clicks and build brand recognition.
The cost per click for Google Display Network ads is low when compared to Google Search Ads.
For example, the cost per click for a floor cleaning firm in search display network advertisements for a specific term like “floor cleaning near me” is roughly $4-5. Meanwhile, the CPC for Google Display Advertising might be as low as $0.05.
You may receive dozens of clicks on google display ads for the price of one click on a search ad.
As a result, Google Display Ads might be a great alternative for advertisers on a tight budget.
Enhanced reach
Each resource category allows uploading numerous resources (for example, multiple headlines, logos, videos, and images). Google’s advertising automatically adapts in size, style, and format to match almost any available ad space. Responsive display network ads, for example, may appear as a banner ad on one site and as a dynamic text ad on another.
What is the difference between Google Search Network and Google Display Network?
Unlike the Google Search Network, where businesses place text ads in the search engine results, on the GDN, businesses put display ads on a vast network of sites across the internet.
What sites are on the Google Display Network?
The best thing about GDN is that it has an enormous reach.
According to Google, the Display Network reaches over 90% of internet users globally across millions of websites. This includes:
- Gmail
- YouTube
- News Outlets: News.com.au, Daily Telegraph, The Guardian
- Blogs: Timeout, Lifehacker, Pedestrian
- Informational websites: WebMD
- Shopping: eBay, Gumtree, Domain
Simply put, if you want to get your advertising seen anywhere on the internet, there’s clearly only one place you should go to, the Google Display Network.
Quick guide to Google Display Ad Sizes and Formats
Another massive advantage of using Google Display Network is its versatility. The variety of Google display ad sizes and formats is enormous, including text ads, image ads, rich media, static and animated image ads, and video ads.
Here are a few examples.
According to Google, the best performing Google Display ad sizes are:
-
Medium Rectangle (300×250):
Performs best when embedded within text content or at the end of articles.
-
Large Rectangle (336×280):
Like the medium rectangle, this performs well when embedded within text content or at the end of articles.
-
Leaderboard (728×90):
Best when placed above main content, and on forum sites.
-
Half Page (300×600):
Offers rich user engagement and is one of the fastest growing sizes by impressions.
-
Large Mobile Banner (320×100):
Offers twice the height of Google’s standard mobile leaderboard.
The best Google display ad sizes and formats are:
-
250 x 250 – Square
-
200 x 200 – Small Square
-
468 x 60 – Banner
-
120 x 600 – Skyscraper
-
160 x 600 – Wide Skyscraper
-
970 x 90 – Large Leaderboard
-
320 x 50 – Mobile Leaderboard
Now that you know what the GDN is and the different ad types and sizes available, let’s dive into how to use the GDN for businesses.
How to use Google Display Network for businesses
1. Laying the groundwork
When it comes to Google’s search network vs display network, there’s one huge difference: on the search network, users are in a seek mode.
They are actively searching for a solution to their problem; in other words, their intent to find information is more direct.
The display network, on the other hand, is more passive.
You are showing ads on external sites that people are visiting for some other specific purpose. They aren’t there searching for your product or service.
This means your approach to ads on the GDN needs to be very different from those on the search network.
For a start, you really need to understand WHO your ideal customers are, WHAT they are searching for and HOW they are searching.
Otherwise, your ads won’t be targeted to the right people, on the right websites and they won’t grab their attention.
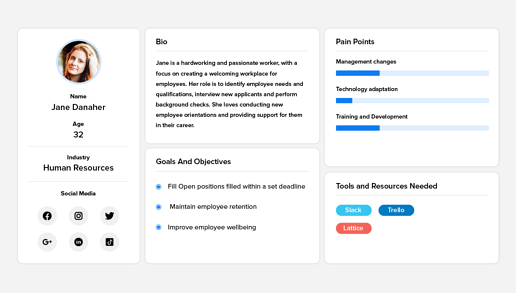
The best way to do this is to create buyer personas.
Buyer personas are a semi-fictional representation of your buyers that zones in on your ideal customer’s goals, pain points, objections, and other unique characteristics.
Do research with your sales team, customer service team and real-life customers.
Then use persona builder tools, like HubSpot’s Make My Persona, to consolidate your research.
It might look something like this:
2. Choosing keywords
Next, research which keywords you should be targeting.
You need to understand the buyer’s intent in order to do smart keyword research.
That’s where your buyer personas come in.
Do some research around the following:
- Which keywords your ideal customers type into Google, to find a product or service like yours.
- Keywords related to your product or offering
The Google Keyword Planner tool is a great way to do this research.
Start with a small list of keywords to see what kind of placement and traffic volume you get, then introduce more keywords and remove some as you learn what’s working and what’s not.
For more information, consult our comprehensive guide to keyword research.
PRO TIP: A lower cost per click (CPC) isn’t always better.
Because Google Ads works in an auction system, the price fluctuates depending on how much advertisers are willing to bid.
When bids are higher it’s likely (not guaranteed) they can afford to bid higher because the ad is more likely to convert and turn into a sale – and therefore produce a good ROI.
3. Setting up an ad
Setting up your display ad campaign in Google Ads is pretty easy – but there are a few important steps you need to pay attention to if you want true success.
Before you create ads, you need to get clear on your objective.
- What do you want people to do when they see your ad? i.e. what does a conversion mean to you?
- Where you will send traffic for them to convert?
Typically, the best approach is to set up a landing page that is highly relevant to the ad and designed to convert.
Landing pages refers to the pages that users arrive at after clicking your ad. To drive traffic on your landing pages, you can set up a display advertising campaign with relevant ads.
Once you’ve got that sorted, sign in to Google Ads Account and follow these steps:
- Choose ‘Display Network Only’ from the campaign options.
- Select a marketing objective.
- Decide the location targeting for your campaign.
- Set your ad budget – this is how much you are willing to spend on your ads per day. Go for Manual CPC bidding to start, as this gives you more control. Then, you can always experiment as you learn the ins and outs. Start with a low bid and adjust it later (Google Ads gives you an idea of what you should be bidding).
- Pick Ad extensions, such as call extensions.
With the basics ready, you can move onto audience targeting.
If you’re wondering how long it will take to see results on Google Ads, aren’t sure if inhouse or outsourcing your Google Ads campaigns is right for you or looking for more ways to experiment with Google Ads, see our linked guides for more ideas.
4. Targeting
How do you reach the people you know are most likely to be interested in your products or services? Through targeting.
This is absolutely essential to any successful display ad campaign, as otherwise you are wasting precious budget on people who will never convert.
With Google ads demographic targeting, you may reach a specific group of possible consumers who are likely to be within a certain age range, gender, parental status, or family income. For illustration, if you have a women-only fitness installation, demographic targeting might help you avoid showing your advertising to men.
Digital marketers are nowadays using rich media ads to target both desktop and mobile users.
Rich media is a word used in digital marketing to describe an ad containing advanced features such as video, music, or other aspects that encourage viewers to interact and engage with the content.
While text advertisements sell with words and display advertising with images, rich media ads provide more methods to engage an audience with an ad.
Google Display Network offers different targeting methods, which you can experiment with to see what works best for your ads.
Let’s take a look at the targeting methods and how they work.
Understanding Google Display Network Targeting Methods
Tip #1: Remarketing
If you want to see a great return on the display network, remarketing is the first place you should start.
Remarketing is where you track people who have previously visited your site or taken a specific action on your site, and follow them with ads on various sites they browse.
It works because the people you’re remarketing to have already demonstrated a genuine interest in what you have to offer by visiting your site.
The brilliant thing about remarketing with the GDN is that you can get really granular.
For example, Google lets you target your ads purely to people who stayed on your website for more than X minutes. These dynamic search ads target customers who are already in the market for your products or services, ready to buy at the exact moment they see your ad.
Set up multiple remarketing lists based on different actions people took on your site, the products or content they’ve shown interest in, and more.
Here’s a remarketing dynamic image ad for news.com.au on the taste.com.au website:


What we love about this ad is the really strong call to action, promoting the viewer to download the free app now.
Retargeting ads are for WARM traffic, but display network ads can also be exceptionally effective at engaging COLD traffic.
This is where you should really pay attention to the targeting criteria.
Here are a few more targeting strategies:
Tip #2: Placement targeting
Managed placement is the only targeting method that gives you granular control over exactly where your ads are being shown on the Google Display Network.
The big pros are that you can target a specific demographic and zone in on niche websites and forums that match the interests of your target audience. You’re not relying on Google to do the decision making – you choose the sites based on what you know is relevant to your audience.
This means conversions tend to be more consistent and cost less as a result.
One strategy is to identify just 5-10 domains that are hyper-relevant to your product or service and start serving up ads on these sites first. Measure the results and if you’re not getting the conversions you want, expand to other sites.
How do you choose the right sites?
One way is to check where referrals are coming from on Google Analytics:
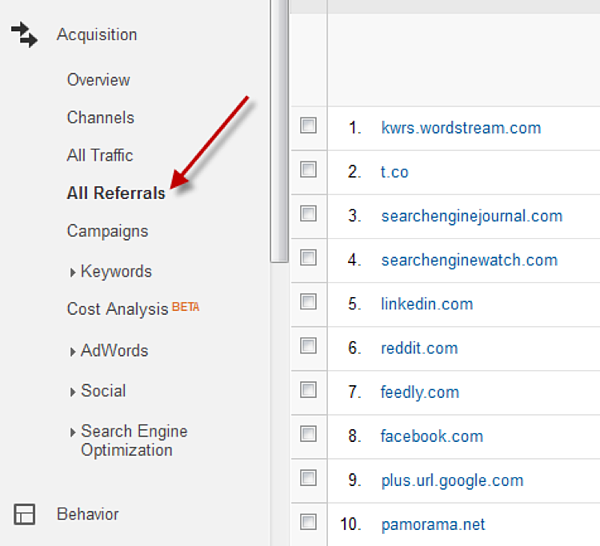
Image credit: Wordstream.
Tip #3: Contextual targeting
This is the most popular type of targeting for the GDN. It’s where you use the keywords related to your products/services.
First, you create a keyword list, then Google will optimize your display ads to appear on sites relevant to those keywords.
You will end up appearing on websites you may not have otherwise considered. However, you will need to keep a close eye on the list of sites to check if your ads are hitting the mark.
Tip #4: Topic targeting
Select from an existing list of page topics and your ads will only display on pages about that topic.
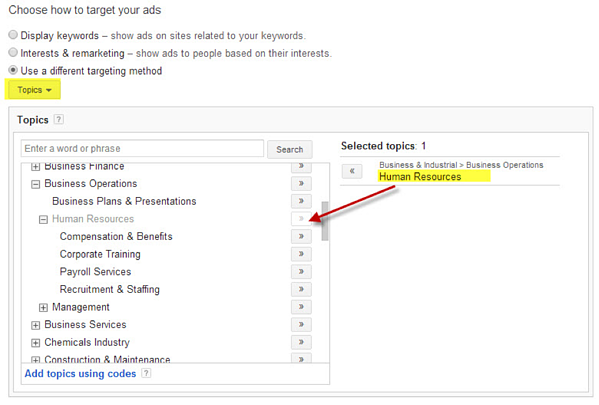
Image credit: Medium.
Take this example on AllRecipes below:
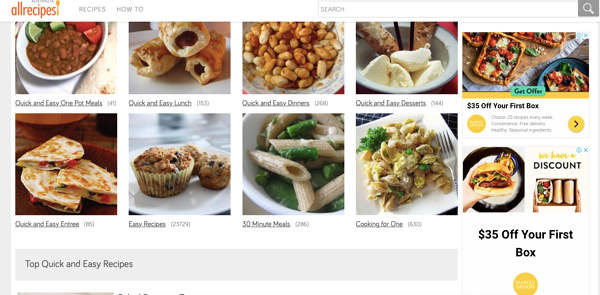
We can assume the meal delivery company has selected the cooking category, meaning its ads are displayed on recipe sites.
It makes complete sense to see this ad on the “easy recipes” page, as they are targeting people who want a quick and easy meal solution.
What we love about this display ad is that they provide an enticing offer to get viewers to click.
The main problem with this targeting method is that you can’t drill deep into the topics and may wind up with your ads on unrelated sites.
The solution is to combine topic targeting with another targeting method to make sure you are reaching potential customers.
Tip #5: Interest targeting
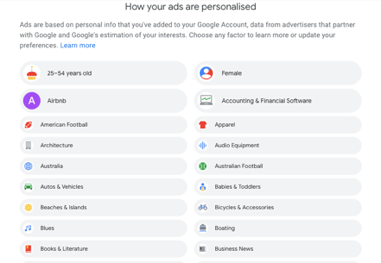
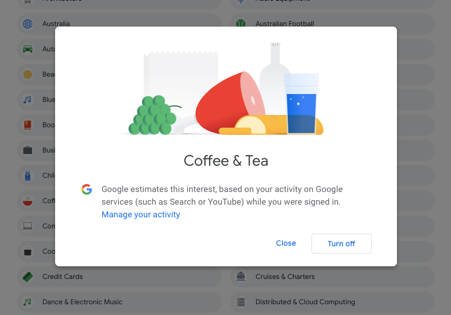
This might seem a lot like topic targeting, but actually it’s very different. Interest targeting lets you target the user, not the page content. It works using cookies, which are stored on users’ computers every time they visit a page within the GDN.
If someone is regularly visiting sites in a particular category, they will be added to the list of people Google says are “interested” in that category.
Because of this, the user could be looking at anything when your ad appears, so long as they’re on a site within the GDN.
You can view the information Google has collected about you under “My Account.”
Combining different targeting methods
Because of the pros and cons of different targeting methods, the tried-and-tested approach is to combine them.
You can include an ad group in your marketing strategy to widen the reach of your campaign. An ad group consists of one or more adverts with related goals.
Each of your campaigns has one or more ad groups that may be used to arrange your adverts based on a similar subject. For example, consider categorising an ad group based on the various product or service kinds you provide.
When you apply more than one targeting method to an ad group, your ads will only display to people who match BOTH targeting criteria.
While you’ll get less impressions for your ads, you’ll know your ads are shown to people who really fit your ideal customer profile.
For example, you could use Topic AND Interest Targeting.
To clarify, if a user visits a site within the topic you select AND they’re also in a matching interest category, you know the user consistently reads that content. This ensures that you have a higher chance of engaging the right type of visitor than if you used either topic or interest alone.
How to create a Google Display Ads Campaign
Okay, then! Now that we’ve addressed all of the technical stuff of Google display ads, let’s have a look at some of the best practices you can put in place to optimize your returns and run a successful google ads campaign:
1. Make use of your top-performing search terms.
Keyword targeting is an excellent approach to kickstart the google display ads campaign presenting your company to the right people.
If you want to give display advertising a shot but aren’t sure where to begin, we recommend starting with your top-performing search phrases. You may target specific websites which have a similar app, as your ad may appear there as well.
Of course, the definition of “top-performing” is up to you, but if there are a few terms that consistently deliver low-cost clicks or conversions on the search network, why not give them a chance on the display network?
True, customer intent on the two networks is really different.
However, suppose your search advertising is generating hits and conversions. In that case, you can be confident that the keywords behind them are winning.
2. Make use of bid modifications
After a period of running your display campaigns, you’ll have enough data to make educated performance decisions—which keywords are doing well, which custom affinity audiences are performing poorly, and so on. Bid adjustments, which may be made at the ad group or campaign level, enable you to transform performance judgments into strategy.
When you set a positive bid adjustment on an ad group, you are instructing Google ads to raise your maximum CPC bid anytime one of the ads in that ad group is eligible to appear. Similarly, when you make a hostile bid adjustment, you instruct Google Ads to lower your maximum CPC bids for that ad group.
Simply said, implementing bid adjustments is an excellent strategy to increase your profits from top performers while decreasing your losses from weak performers and increasing brand awareness.
3. Examine your referral traffic
Google Analytics is chock-full of valuable data. The referral traffic report (found under Acquisition > All Traffic) is quite helpful for display advertisers. The referral traffic report essentially shows you which websites are most frequently connecting to yours. Put another way, it shows you which websites appeal to those who could benefit from your product or service.
These websites are ideal for displaying your display ads. You can be sure in driving returns on those impressions and clicks since you know you’re advertising to appropriate audiences.
4. Highlight your value proposition.
Your prospects may scroll through your display ads without even noticing them since they are so accustomed to seeing them at this stage.
To avoid squandering opportunities—as well as money if you’re bidding on a cost per thousand impressions (CPM) basis—critical it’s that your display advertising capture the attention of your prospects.
Obviously, the visual aesthetics of your advertisements—colour scheme, typeface, and so on—play a significant role in this. What is less evident is the role of your value proposition.
Simply said, your value proposition is the advantage someone will receive if they become a client of yours. If you’re selling a pair of men’s boots, your value proposition may be the increased confidence one gets when he looks nice.
Make your value proposition stand out on the page, no matter what it is.
5. When writing RSAs, pay attention to the headlines.
You’ll be asked to compose four bits of copy when designing responsive display ads:
- A brief summary (25 characters)
- A lengthy headline (90 characters)
- A description (90 characters)
- Your company’s name (25 characters)
You should know two things about headlines: (1) Google Ads will never run both simultaneously; (2) Google Ads will occasionally omit your description. There’s no assurance that any headline you choose for a specific iteration of your RSA will be followed by your description.
The takeaway: It is advisable to run relevant ads to target specific websites. While creating a Google ads campaign, make sure that your headlines are compelling enough on their own. Both should convey the distinct value of your company or the deal you’re offering.
Optimising your ads on Google Display Network
How can you make sure you’re getting the absolute best return from your display ad campaigns?
You need to give your display campaigns the same love you’d give search ads (or any other digital channel).
Take time to review their performance on a regular basis, especially if you are using the automatic placements.
Use the top KPIs to measure and manage your Google Ads. Then adjust your targeting, budgets and creatives based on the insights.
Use this actionable optimisation checklist:
1. Exclude irrelevant audiences
Part of understanding WHO your dream customer is also includes understanding who they are NOT. We’re talking about a negative persona.
On Google Ads, you can exclude audiences that are not relevant to your business, which helps you reduce your costs and increase the likelihood that your ad will attract clicks from the right people.
2. Exclude irrelevant categories
Just as you can target placements in the Google Display Network to show your ads, you can also exclude categories and placements where you don’t want your ads to show.
3. Exclude mobile apps
Is showing your ads in games and music apps beneficial to your brand? Probably not.
When someone is in a mobile app, they’re either looking to entertain themselves or perform a very specific task.
If someone clicks on the ads, chances are they did it by accident – which can quickly tank your budget.
Stop wasting money on accidental clicks and exclude mobile apps from your campaigns.
How to exclude mobile apps:
Go to your Google Ads dashboard, select the “Placements” tab, then click to “Exclusions.”
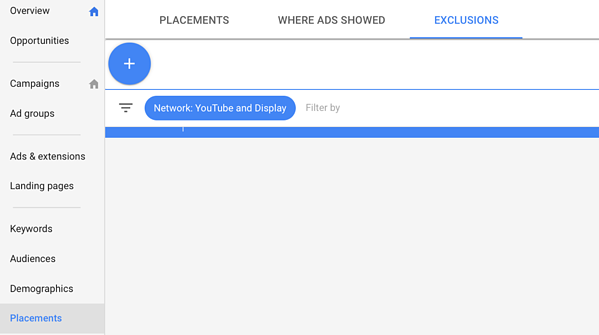
Click “Add placement exclusion”, then enter the names of any apps or sites you want to omit.
In addition to the big ones, go to Google Analytics to see if other apps are sending you high amounts of clicks.

4. Review ad performance
Review your ad performance and exclude what isn’t working. For example, if your ads aren’t performing well in specific geographic regions, exclude these regions from your campaigns. Then optimize as many ad groups as possible.
5. Use click to call extension
Adding a phone number to your ads can significantly increase click-through rates. This simply means that when your call extension shows, people can click a button to call your business directly.
Using a click to call extension translates to more customer engagement with your ads and a higher chance for instant conversions.
Over to you
This guide hasn’t covered every single thing you can and should do with Google Display ads. It’s about giving you the essential information you need to get started right now.
You’ve learned how the Google Display Network works, how it can help you reach more of your ideal customers, and the things you need to do right now to kick off an ad display campaign.
We know it can be overwhelming. That’s why if you need help getting started with the Google Display Network, or want to talk to PPC gurus about creating a long-term growth strategy, we’re ready to help.
We’re offering you a Digital Audit and Strategy Session. Usually this offer is worth $2,000, but today we’re offering it for FREE.
We’re willing to give away such tremendous value because we want as many businesses as possible to benefit from the power of Pay Per Click.
This offer includes one of our expert Digital Gurus auditing your current digital and search presence. Your Guru will quickly uncover core growth opportunities and map the way to fast and targeted results. Click below to find out more!